The task for rubber manufacturers is to identify rubber additives
that con be used either singly or in conjunction to produce rubber
parts to a high quality and with the high levels of ozone resistance
needed for a long service life. Examples of the types of product for
which this is expected include windscreen wipers, door and window
seals, and, of course, tires. Accelerated static and dynamic tests
can be carried out in a chamber with a controlled ozone dosage that
is monitored to ensure compliance with standard test conditions.
Performances of rubber compounds and additives are assessed through
comparison of both appearance and mechanical properties after
various levels of ozone exposure, for various times, as specified in
testing procedure.
- Basic principles
- Figure 1 shows an example of a chamber for the determination
of a rubber's resistance to ozone cracking under static and
dynamic conditions according to DIN-53509, ISO-1431-1 and
ISO-1432-2.
-
- Components
- Repeatability of ozone cracking results can only be guaranteed
if reliable ozone monitors, ozone generators and well-vented
chambers are available.
- Ozone monitor
- Anseros has been a leading manufacturer of ozone analysers for
the last 17 years. A non-dispersive ultra-violet monitor (NDUV)
is used for rubber testing that operates using the one-beam
principle. Sensitivity drift cannot occur since automatic zero
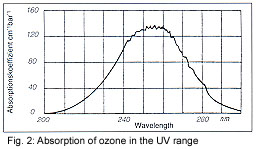
adjustment is made by a built-in microprocessor. The absorption
of UV light at a wavelength of 254nm (Fig. 2) is put to
practical use in the NDUV ozone monitor produced by Anseros. The
unit can be made to measure ozone concentration in volume terms
as parts per million (ppm) or parts per hundred million (pphm).
Alternative measurements in terms of mass concentrations of
micrograms per cubic metre (ug/m3) or milligrams per cubic metre
(mg/m3) are also possible, using a conversion based on the
formula:
- Conc. O3(mg/m3) = Conc. O3(pphm) x P/T x 10
-3
- (Where P equals pressure in hectaPascals (hPa) and T equals
temperature in degrees Kelvin).
- Ozone generator
- Ozone can be generated from ambient air using either a UV lamp
(Anseros
Peripheral COM-UV-PID) or via corona
discharge (Anseros Peripheral COM-GD-PID). The
UV lamp principle is simple to use and offers a high level of
stability, however the ability to provide capacity control for a
corona discharge tube is much greater. The volume of ozone that
has to be generated depends on the following:
- Set point of ozone concentration
- Temperature
- Mass of rubber material
- Humidity
- Dust
- Other organic contaminants
In either case, both methods of extracting the ozone from ambient
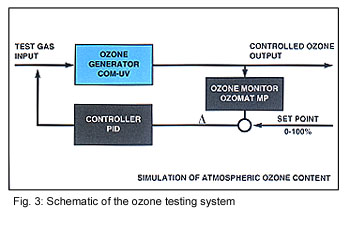
air have to be controlled. To achieve this control. Anseros has
developed a special digital PID control with feedback for its ozone
test chambers (Fig. 3).
 詳細資料請參閱相關網頁
ANSEROS OZONE PRODUCTS
詳細資料請參閱相關網頁
ANSEROS OZONE PRODUCTS
|
|
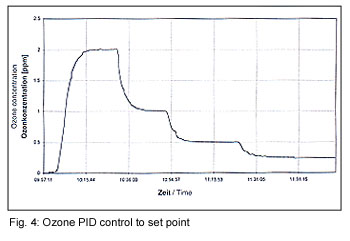
The Anseros PID ozone control unit provides for easy sampling and
monitoring of the ozone concentration in the cabinet. The ozone
concentration is increased on an asymptotic curve to the control
setpoint to prevent the rubber sample being exposed to higher levels
of ozone that would cause premature failure and inconsistent results
(Fig. 4)
- Ozone test chamber
- Anseros only manufactures stainless steel inlets available in
volumes ranging from 35 to 8,000 litres. The air velocity inside
the chamber reaches 600 mm/sec driven by an additional fan. The
operation of the cabinet is according to DIN-53509, with air
inside the chamber being replaced three times per hour (or as
demanded in DIN standards for other volumes of test chamber),
and the required ozone concentration being achieved within 30
minutes from the commencement of the test or change in setpoint
(NB: ASTM requirements slightly differ from this). Generally,
four types of static and dynamic test equipment can be installed
in Anseros ozone chambers:
-
Static test without rotation
-
Dynamic test without rotation
-
Static test with rotation
-
Dynamic test with rotation
If the test equipment that is necessary to carry out
rotating dynamic tests in installed in the chamber, the chamber has
the capability to carry out the other three forms of test. The
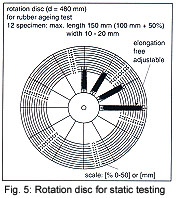
rotation disc procedure guarantees that test conditions to ISO-1431-1
are met for every sample that is tested. Fig. 5 shows a rotation disc
for 12 samples, along with a scale to indicate sample extension. The
rotation frequency is 12 rpm in accordance with ISO 1431-1, but
alternatively can be set to individual customer specifications. A
typical standardised ozone test chamber is shown in Fig. 6. The
chamber of this machine has a capacity of 50 litres, is equipped with
an Ozomat MP6080 ozone monitor, a digital ozone generator, a PID
controller and an ozone concentration, temperature and humidity
recorder. The unit is designed and fitted out for undetectable
mounting.


|